| Operator | Spectrum |
| Wataniya Telecom | band 3 (1800 MHz) band 8 (900 MHz) |
| Zain | band 3 (1800 MHz) and band 8 (900 MHz) |
| Viva | band 3 (1800 MHz) and band 8 (800 MHz) Band 7 (2600MHz) |
Vodafone HSPA+ 3G 4G USB Surf Stick
As the world’s top network provider, Vodafone is always leading the new trend in the telecom industry and Vodafone usually let his customer first to enjoy new experience and new technology from the surfing.
Vodafone USB Sticks are well known all over the world and since unlocked sticks are not limited to Vodafone network, we could see Vodafone surf sticks are used worldwide. Today, let us see the HSPA+ USB Sticks from Vodafone.
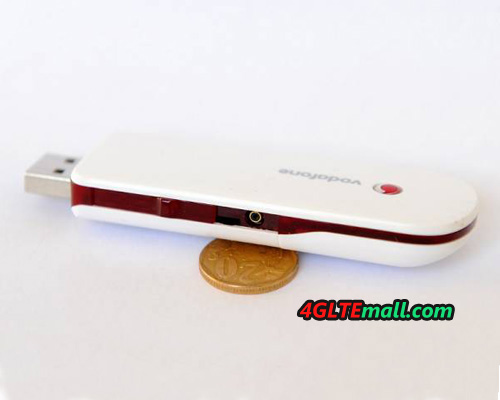
Vodafone K4505 3G HSPA+ 21Mbps USB Stick
Vodafone K4505 HSPA+ 21Mbps 3G USB Surfstick is one of the hot unlocked HUAWEI 3G Wireless USB modems, which allows users to download at 21Mbps and upload up to 5.76Mbps. What’s more the modem could be upgraded to support 28.8Mbps download speed.
It includes the ability to roam globally on HSUPA, HSDPA, UMTS and GSM/EDGE networks. You can stay connected wherever your travel schedule takes you. With External antenna, it could work with better signal even when you are in rural area.
Vodafone K46053G DC-HSPA+ 42Mbps USB Surf stick
Vodafone K4605 is the second HSPA+ mobile broadband after K4505, and it’s come from the factory model HUAWEI E372, but seems better than E372. K4605 supports even more, it is twice speeds as HUAWEI K4505, HSPA+ download speeds up to 42Mbps, also the fastest dongle of Vodafone, additional, unlocked K4605 has another features difference from others that’s the bands support, generally supports 900/1900MHz, but this one support whole band.
Unlocked Vodafone K4605 modem removes the network lock that prevents the modem from working with other mobile network operators. Once unlocked, the Vodafone K4605 modem will work with mobile broadband operators all over the world, Including Vodafone, Telefonica, Movistar, O2, Orange, T-Mobile, AT&T, TIM, Three, Wind, Claro, Rogers, Telstra, Optus, Virgin, Airtel, 3, Cingular and many more GSM and UMTS mobile networks
Vodafone K50054G 100Mbps LTE USB Surf stick
Vodafone K5005 4G LTE 100Mbps USB modem (the original factory model is Huawei E398), is a newest Triple-Mode LTE Modem from Huawei devices. It’s fully unlocked and ready to use with all global services. Since Vodafone K5005 is for Vodafone 4G LTE network, it supports maximum 100Mbps download speed and 50Mbps upload speed.
Telecom also sells the device as well, and it’s called Speed Stick LTE. The difference of them is just the logo. Vodafone K5005 is the upgraded version of Vodafone K4605 and support 4G LTE network, while the latter only works on 3G DC-HSPA+/HSUPA network. And K5005 LTE USB Stick is the first LTE model released by Vodafone to benefit the customer who has higher demand for the speed.
Vodafone K5006Z 4G LTE 100Mbps USB Surfstick
Vodafone LTE USB-Stick K5006z is a new 4G LTE USB modem that produced by ZTE, the top telecom equipments supplier in China. K5006Z is one model upgraded from Vodafone 3G USB Stick, such as K4605, K4505, K3765, K3565, so it has the similar appearance as them. There is twin model Vodafone K5006H which is produced by HUAWEI, also the head wireless terminals supplier in China.
Vodafone K5006Z and K5006H are only the manufacturer difference. The other features are almost the same. Vodafone K5006Z supports LTE frequency at 800MHz and 2600MHz with up to 100 Mbps download speed, in the UMTS network, thanks to DC-HSPA+ up to 43.2 Mbps in download possible. Unlocked K5006z could work around all over the world with the providers in Asia and Australia.
Vodafone Connect Pen K5007 4G 150Mbps LTE USB Stick
Vodafone Connect Pen K5007 4G LTE USB Surfstick is the latest Vodafone 4G USB Surf stick for LTE network. It’s first released in Portugal and it support 4G LTE download speed at 150Mbps (the fastest and maximum download speed based on current 4G technology).
Vodafone Connect Pen K5007 LTE FDD stick is the world’s first commercially available device for LTE Category 4. It comes from the factory modem HUAWEI E3276 4G LTE Surfstick with Vodafone brand.

Vodafone Connect Pen K5007 4G USB modem supports a total of five frequencies (800/900/1800/2100/2600 MHz) and delivers up to 150 Mbit/s downstream and 50 Mbit/s upstream. K5007 4G Dongle also supports DC-HSPA+ UMTS network with GSM and EDGE backward. The dual-carrier HSPA+ data rates of up to 42 Mbit/s can be achieved.
It would be lucky if you are under Vodafone network, but if now, there is still ways to enjoy same network experience. There are unlocked surf sticks available on www.4gltemall.com . With unlocked ones, you don’t need the contract with Vodafone and still enjoy HSPA+ fast speed freely.
LTE Versions: TDD and FDD
LTE is available in two technical variants: TDD and FDD. TDD stands for the English expression Time Division Duplex.FDD stands for the English word Frequency Division Duplex. It sounds complicated, but you can explain it simply: When FDD there are two channels, which is broadcast on: on one which you receive messages with their laptop or smartphone and on the other which you send the message. In TDD there is only one channel – it will be used alternately to send and receive. Transmit and receive mode switch it so fast that you do not notice. What are the advantages and disadvantages of both techniques?
The advantages and disadvantages of the techniques
FDD seems better at functions where many data are simultaneously transmitted and received – they both have their own supervised channel. One example would be telephone calls or video calls. Another benefit: When building the base stations need to take any further precautions – as transmit and receive channels are different, disrupt the channels of two base stations are not mutually exclusive. In TDD networks have to ensure that adjacent base stations do not interfere with each other.
Conversely, TDD uses the available space in the radio room much better. Often more data is received than sent, or more sent than received – for example, if I put a video on the Internet or send a friend a photo collection. In these cases – in technical terms, these are asymmetrical applications – TDD divides the space to send or receive on demand. Overall, the introduction of this TDD technology is cheaper, among other reasons, because the mobile operators do not have to hire as much radio room from the state as in FDD. The TDD needs only one channel and not two. For operators who previously used the wireless technology WiMAX, the transition to LTE TDD, with a lower price.
FDD and TDD: Worldwide both lay sometime par
Currently, the FDD technology is well forward, but with increasing global expansion of LTE networks, two techniques are commonly used equally well. The currently existing LTE networks in Germany, Austria, Scandinavia and the Baltic use FDD-LTE. Even Verizon Wireless in the U.S. uses this variant.
However, LTE is in TDD variant currently being tested by E-Plus in Germany. LTE TDD has also been tested in France, Ireland, Poland; the United States has the Wimax operator Clearwire tested. And WiMAX is interested in the technology in Japan, Saudi Arabia, Oman and Taiwan.
In South Korea, the Korean SK Telecom in early July has taken a LTE network on TDD base into operation in Malaysia still 2011; a TDD-LTE network will be built. Russia wants the operator Yota use a nationwide 180 cities comprehensive LTE network TDD. Experts believe that China has in each case; the TDD variant will be used for LTE, as well as in India.
Real 4G LTE Advanced Technology and the Future
Since November 2008, under the name IMT-Advanced, LTE and WiMAX are the specifications for the fourth generation of mobile. The International Telecommunication Union (International Telecommunication Union, ITU short) set these requirements.
Since October 2009, two technology families apply for the title of 4G wireless data technology of the future, according to the International Telecommunication Union. Firstly, there is the advanced technology LTE Advanced, which evolutes from LTE. Second, the applicant is provided with the bulky abbreviation IEEE 802.16m technology, which has evolved from the WiMAX group.
Colloquially LTE or Mobile WiMAX is already now referred to as 4G technologies. In colloquial usage, technical standards, there are 3G systems.
The ITU standards: A gigabit per second is the goal
Some key requirements on wireless technologies of the fourth generation: Higher transmission rates, greater bandwidth, high spectral efficiency and low latency and better coverage of the peripheral areas in the radio cells are crucial criteria.
As research targets for the transmission rate is at 100 megabits per second per the International Telecommunications Union, and gigabit per second high with low mobility. There are also up to 40 megahertz scalable bandwidth for the transmission channel, but the researchers are encouraged to draw bandwidths up to 100 MHz considered. The spectral efficiency is measured by measuring the transmission rate per bandwidth. The ITU for IMT-Advanced set 15 bits per second per hertz (bits/s/Hz) on the downlink and 6.75 bit / s / Hz in the uplink.
As examples of different high top speeds in different widths, radio channels are given by the ITU on a channel of 40 megahertz (MHz) 600 Mbit/s and on a channel of 100 Megahertz 1500 Mbit/s respectively in the downlink.
The 4G LTE-Advanced candidate
The bandwidth is LTE-Advanced is significantly higher than the 3G. Instead of 20 megahertz, LTE-Advanced can bundle multiple carriers and thus use up to 100 MHz simultaneously. It is also possible that frequency bands in different frequency ranges are combined, since no operator has been on a continuous frequency range of 100 MHz Currently these 100 MHz are only theoretically achievable, in practice more spectra has to be assigned. This can happen only in 2015 at the World Radio Conference (WRC). Until then, the bandwidth will probably be limited to 40MHz.
Another innovation that could keep up with LTE-Advanced collection is called “relay nodes”, i.e. relay stations. This will allow, even outside the range of a base station to receive the signal. In the edge region reinforce the signal relay stations. Connected the relay stations are connected to the base station. Thus, the signal strength inside buildings can be improved.
Increase the spectral efficiency
The concept of multiple antennas (MIMO: Multiple Input / Multiple Output) technology, which is already partially used, will also be expanded. Instead of two antennas at the transmitter and receiver (2×2 single-user MIMO) to be introduced up to eight antennas for the downlink (8×8 single-user MIMO). For upload, still four antennas are used. Simultaneously by using multiple antennas, a plurality of data streams on the same frequency is transmitted. This not only increases the spectral efficiency, but also the transmission quality.
When the spectral efficiency of LTE-Advanced will even peak values of up to 30 bits/s/Hz can be achieved in the download as well as 15 bits / s / Hz in the upload. LTE has the merit to 15 bits / s / Hz when receiving and at 3.75 bits / s / Hz when sending data. This shows that, although LTE in terms of spectral efficiency can already meet the requirements of IMT-Advanced, but only in the download. The upload, and in the range, it is far from being a 4G technology.
4G: colloquial and technical language
Although often LTE or Mobile WiMAX called 4G technologies, they are from the standpoint of technical standards only further developments in the field of 3G and provide an intermediate step represents some criteria for IMT-Advanced are indeed fulfilled to some extent, by no means all.
Nevertheless, the marketing departments of international mobile operators call the new LTE technology, which is increasingly used in the United States, even as 4G, to illustrate the difference in the speed of data transmission in comparison to UMTS networks. It is becoming apparent that this usage was soon penetrated. Then LTE or similar technology, such as Mobile WiMAX are commonly referred to as 4G technology, and only in the jargon of technical standards still out as 3G technologies.
LTE Technology
The new mobile technology LTE is superior to the existing mobile technologies GSM and UMTS, the link speed which data is transferred is much far higher the response time of the current system and the connection is faster.
This is achieved through a variety of improvements in various areas of technology that each contribute in itself to significantly better overall picture of the data radio technology. Due to the significant improvement in overall performance, LTE mobile technology is increasingly recognized as the 4th Generation (4G) refers. While in technical descriptions of the generation LTE 3.9 is assigned, but the name of LTE as 4G mobile technology is likely to prevail worldwide.
Improvements in wireless technology
A number of technical innovations allow use of the available radio room better. The OFDMA radio technology allows customizing the transmission capacity to meet the needs of each user – who wants to watch TV on the mobile Internet, gets more space than someone who just wants to make calls only. The downlink OFDMA is used for the same transmission speed with a very small range of the radio room – it takes up less space for an equal amount of data transmitted. Also known as High Speed OFDM Packet Access (HSOPA) technology uses the existing radio room two to four times better than the method called Wideband Code Division Muliple Access (WCDMA), which is used in HSDPA.
With the multi-antenna MIMO technology can be transmitted simultaneously with the current standard of four antennas and received simultaneously – what the reception improves performance significantly. Moreover, a possible interference by neighboring radio waves, which prevents so-called interference significantly stronger.
All in all, the radio room with LTE is better used, because the signals from the multiple antenna technology at transmission and reception are separated in space, and because the size of the radio channels can be adjusted according to the user.
Improvement in network construction
There are also improvements in network construction. The networks as a whole should be fit. In the network architecture, the requisite leaner architecture makes first by the absence of an element – namely the mediator between the base station and core network noticeable. The significantly higher amount of data that can be processed thanks to improved techniques the radio part of the network, of course, lead to the fact that mobile operators must also provide the lines between the base station and core network for more capacity.
Overall, the whole network will be improved so that its response times are less than five thousandths of a second (milliseconds). After all, only at a very low response time (latency) of the network can be demanding services such as Mobile TV, video calls and mobile online games provide no problems.
The competition techniques: Ultra Mobile Broadband and Mobile Wimax
LTE is the view of IT expects to be the first mobile technology, which works worldwide as a general standard. Nevertheless, there were – from a technical viewpoint – two other data transmission technologies that were considered LTE competitors: Mobile WiMAX and Ultra Mobile Broadband are techniques that offer similar data transfer speeds as the mobile technology LTE.
Ultra Mobile Broadband was a technology that is used in the USA the third mobile communications standard Should develop a rapid generation CDMA2000 mobile fourth generation. Above all, the U.S. chip maker Qualcomm invested diligently in the development based on CDMA 2000, while the Swedish Ericsson continued to LTE as a new cell phone technology. Both technologies used very similar approaches. In November 2008, Qualcomm ended its funding of research and waved a UMB to LTE.
Mobile WiMAX can achieve with the use of LTE and multi-antenna MIMO method on a 10-megahertz radio channel transmission speeds of a total of 90 megabits per second. These are divided in 63 megabits per second for downloading data (downlink) and 28 Mbit/s for transmission (uplink). However, radio cells are in Mobile Wimax achieved with a diameter of one to four kilometers far smaller than the LTE radio cell in the 800 megahertz range – where the diameter is 20 kilometers.
For network design brings dramatic benefits for this difference. LTE takes much less Send master and base stations to build a nationwide network.
ZTE MF23 3G Wireless WLAN Router General Review and Specs
As the follower of HUAWEI, ZTE usually released its wireless products after HUAWEI and sometime, they may look the same. Today, we would like to introduce one Wireless Router from ZTE named ZTE MF23.

Perhaps ZTE didn’t launch much investment and development in stationary 3G WiFi Router, there are few model of 3G Routers to talk about. ZTE MF23 3G Wireless WLAN Router is one new 3G WiFi Router, but it supports HSDPA 7.2Mbps and HSUPA 5.76Mbps, which seems it’s just for common home or office use.
ZTE MF23 3G Router is in very simple and classic design. On the face, there is ZTE Logo and a flower image print on the front, looks cool, and as a part of the lines, the LED indicators are connected to the lines. They are Power, Phone, PPP, 3G and WiFi connection status.
On the top side of ZTE MF23, there is a external antenna, which should be a good tool for the router to get 3G signal. And the external antenna could be r0tated to different angle, so that it could same space or work at the best direction.
On the top side, there are power button to switch the router on or off. Next to the power button, it’s the power plug hole, it’s RJ 11 USB port. This router must get power support externally, there is no built-in battery.

1. POWER Switch: Turn the router ON or OFF.
2. POWER Socket: Connection to the external power supply.
3. WPS: WPS button is used to start Wi-Fi Protected Setup authentication process.
4. Phone: Standard RJ11 connector for Telephone.
5. LAN: Ethernet connections to computer.
6. SIM: (U)SIM port for inserting (U)SIM card.
The 3G Router ZTE MF23 has the function as a telephone, could call out after the telephone cable is connected to it. It work through the 3G SIM card. The most attractive feature of ZTE MF23 should be the Ethernet hole; it could change the 3G signal to support PC via Ethernet cable. If your home has only a few devices, ZTE MF23 should be good choice.
Next the Ethernet port, it’s the SIM slot, you just need to plug your SIM card in, and it would works normally. After your WiFi enabled devices connect with it, you can enjoy the fast speed surfing.
Below are the specifications for ZTE MF23 3G WiFi Router:
* 3G bands: EDGE/GPRS/GSM: 850/900/1800/1900MHz
* 3G bands: HSUPA/HSDPA/UMTS: 850/1900/2100MHz
* Power Adapter specs: Input: 100V~240V(AC), 50/60Hz; Output:+12V (DC), 700mA Max
* Data rate: HSUPA 2Mbps(Max) UL; HSDPA 7.2Mbps(Max) DL
* Indicators: PHONE, PPP, 3G signals, WiFi(802.11b/g/n)
* Standard RJ11 connector for Telephone.
* Manager IP address: http://192.168.0.1(User name: admin, Password: admin)
* Size: 139mm×102.5mm×27.3mm
* Weight: 403g
* OS: Win7,Windows XP,Vista, Linux, Mac OS
Download the ZTE MF23 Specifications and Datasheet.
ZTE MF23 3G Wireless WLAN Router Specifications and Datasheet
HUAWEI B260a Mini WiFi Router has similar functions like ZTE MF23, but it seems that ZTE MF23 is more simple and cool. With a cradle, ZTE MF23 could stand like a tower to radiate the signal and cover the space around you.
The ZTE MF23 is unlocked, so you don’t need to worry about your SIM card can’t work with it, it could support all the SIM card all over the world. If you want to buy one for your home or SOHO office, please check: http://www.4gltemall.com
LTE Speed
The new mobile technology Long Term Evolution (LTE ) promises particularly high rates of data transmission: Both when downloading from the internet, and when sending data, the speed is much faster than the older LTE wireless data technology UMTS with HSPA.
LTE Receiving data
In LTE networks, which are currently being commonly built in Asia and Europe, the operation speeds of theoretically up to 50 megabits per second (Mbit/s) when receiving data are already available. HSPA+, fastest wireless technology in 3G mobile network enables downloading of theoretically up to 43.2 Mbit/s.
LTE may actually even more. However, at speeds up to one gigabit per second (Gb/s) are possible only under laboratory conditions. The data rate depends on several factors. Determined the width of a frequency channel, the amount of data can be sent simultaneously. Several antennas increase in the transmitter and the receiver velocity.
What is the real average speeds will be using LTE in reality remains to be seen. In the U.S. you get in well-developed LTE network of Verizon Wireless at an average speed of about 10 megabits per second and can compete with DSL connections.
The transmission of data
When sending data rates, download can also be achieved, far higher mathematically than the current transmission rate. Technically feasible there are theoretical data rates of up to 86.4 Mbit/s.
Once again, we will have to see how high the rate offered is real then. It is determined by the technology, but also through the utilization of the radio cell or the distance of the user to the transmission tower.
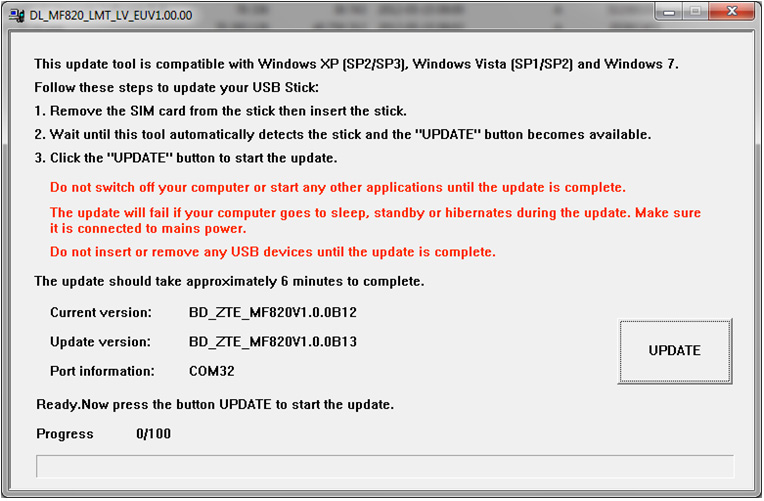
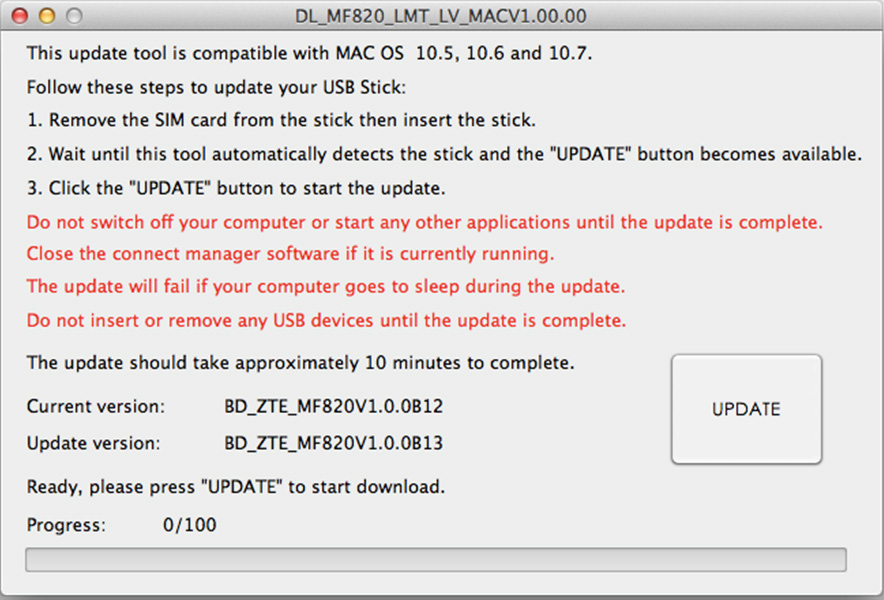
How to Update the Software of ZTE MF820 4G LTE USB Modem?
Since 4G LTE USB modems are more and more popular in users, some users may find their 4G dongles works not as good as they first get them. They may disconnect suddenly or re-connect again, not in stable connection status. At this time, you need to update the software of the 4G LTE USB modem, just like computer, if you use too long time, it would run slow, then you need to re-store the system and you will get new speed.
Today, we would introduce how to update the software / firmware of ZTE MF820 4G LTE 100Mbps USB Modem for Windows OS and MAC OS. It includes two parts because for Windows OS and MAC OS, the software, the software is not the same.
For Windows OS Users:
- Downloading software updates DL_MF820_LMT_LV_EUV1.00.00Setup.7z
- Unzip downloaded file.
- Unplug the modem from the computer, remove the SIM card from the modem and add a modem to your computer.
- Activates DL_MF820_LMT_LV_EUV1.00.00 file.
- Click the button Update.
- Please wait until the complete modem software upgrades. The software update may take up to 6 minutes.
- After the update, reset the previous Mobile Broadbandprogram. PCs with Windows OS Mobile Broadband software can be reset as follows: Click Start> Programs> Mobile Broadband> Uninstall.
- After the previous Mobile Broadband modem software reset is added to insert the SIM card into your computer.
- Wait until the start of the new software setup.
MAC OS X:
- Downloading software updates DL_MF820_LMT_LV_EUV1.00.00Setup.7z
- Unzip downloaded file.
- Unplug the modem from the computer, remove the SIM card from the modem and add a modem to your computer.
- Activates DL_MF820_LMT_LV_MACV1.00.00 file.
- Click the button Update.
- Please wait until the complete modem software upgrades. The software update may take up to 6 minutes.
- After the update reset the previous Mobile Broadband program. In Mac OS X Mobile Broadband software can be reset as follows: click Application> Mobile Broadband click on the Uninstall folder Mobile Broadband files.
- After the previous Mobile Broadband modem software reset is added to insert the SIM card into your computer. Wait until the start of the new software setup.
This is the steps to update the software of ZTE MF820 for Window and MAC operation System, hope it helps you.
LTE Advanced- beyond the next Step
The evolution of LTE (Long Term Evolution) is already developed. LTE Advanced is to say the new technology.
The Third-Generation Partnership Project (3GPP) specifies in its Release 10, the objectives of LTE-Advanced. The mobile technology corresponds to the 3GPP LTE Release 8 LTE Advanced is to be backward compatible. Not only are the transfer rates expected to rise with LTE Advanced. The use of multiple antennas and the incorporation of relay stations are to be carried forward.
More bandwidth
The bandwidth is LTE-Advanced is significantly higher than the LTE in Release 8. Instead of 20 megahertz, LTE-Advanced can bundle multiple carriers and thus use up to 100 MHz simultaneously. Here may also be combined in different frequency bands, frequency ranges – important because no carrier has been on a continuous frequency range of 100 MHz. Currently these 100 MHz are only in theory, in practice more spectra are assigned. This can happen only in 2015 at the World Radio Conference (WRC). Until then, the bandwidth will probably be limited to 40 MHz.
Another innovation that will keep up with LTE-Advanced collection is called “relay nodes”, i.e. relay stations. This will allow, even outside the range of a base station to receive the signal. In the edge region the signal reinforces relay stations. Connected the relay stations means connected to the base station. Thus, the signal strength inside buildings can be improved.
Interference use
Another method that could be introduced with LTE Advanced is CoMP (Coordinated Multi-Point). This is a problem to be addressed, which often occurs, especially in densely populated areas. There where many transmission towers are in a confined space, to their ranges and signals often overlap. This interference occurring far as disorder should be used wisely with the CoMP process. If interference is likely, future base stations preprocess messages for multiple users together prior to transmission. By preprocessing, signals are superimposed on the desired user device design, but are eliminated at the antennas of other users.
HUAWEI E5331 E5331s-2 FAQs
Below is the FAQs of HUAWEI E5331 (also named E5331s-2) Mobile WiFi.