More and more advertisements are introducing 4G to people, declaring a new era is coming. As a consumer, perhaps you may not concern what’s 4G or what is LTE, the top thing you want to know is what I can benefit from 4G. Great, that’s the key point. What can we benefit from 4G?

To explanation simply based on real life experience, you can download a HD movie of 2GB or more in few seconds, you can play complex online games without any interruption and you can transfer large file only a very short while. Yes, 4G can bring us fantastic speed! That’s why the providers are trying to promoting 4G, they finally want you guys to use their 4G devices. Of course, most of time, there would be contract with the devices and you are not free to use other SIM card.

But if you want to use unlocked broadband and SIM unlocked to any operators, how to choose the right model per the preference? Since the most popular 4G device from operator is 4G USB Modem with LTE technology, so we take 4G LTE USB Modem as example to explain, of course, unlocked. Then our question change to: How to choose a 4G LTE USB Modem?

Actually, to buy a 4G USB Modem, just like to buy a mobile phone. Most of the people would consider the brand, Apple, Samsung, HTC are well known and series of phones are optional for almost all the preference. And it’s not hard to determine. But for 4G USB Modem, it seems not that easy…It probably because most of the equipment suppliers are not as famous as the providers and the second reason is that the modems, routers, or other telecom equipments are printed the providers’ logos. Take Vodafone 4G LTE Surfstick K5005 as example, even though the users may use the surfstick for many years, they may don’t know it’s produced by HUAWEI and the HUAWEI factory model is HUAWEI E398.

So the first step to choose a 4G USB modem is to find which brand you prefer. If you don’t know, that would be better to make a decision. Follow me, I will guide you. Someone may ask, may I know how many brands there are all over the world? Ok, it’s time to share, most of us may know SAMSUNG Smartphone, but actually, SAMSUNG is also professional in network solution. So it also has 4G USB Modem available in the market. Some guys may feel good, ok, I like SAMSUNG, I choose it. Don’t be glad so early. After reading the full article, you may feel disappoint. Now I could tell you, SAMSUNG 4G LTE Surfstick is just for specific country and LTE frequency, so it may not be appropriate for you. And the top brands of the 4G USB Modems are HUAWEI and ZTE in China, Novatel Wireless and Sierra Wireless in USA, Option in USA, Alcatel-Lucent, Motorola, LG in Korea also has 4G USB Modem, Pantech in USA is also well known.

At this time, you may feel tired, oh my god, so many options, hard to choose. Yes, there is easy way, follow your SIM card provider and find the unlocked model in the market. Take Telstra 4G LTE Aircard 320u (produced by SIERRA Wireless) as example, if you like it and don’t want to use with contract, you find online store selling unlocked one. Then you are fulfilled.

The premise is that you know this model number, but if you don’t know the model number, how to proceed?
So if you don’t know the brand and provider model, you can follow below steps to determine:
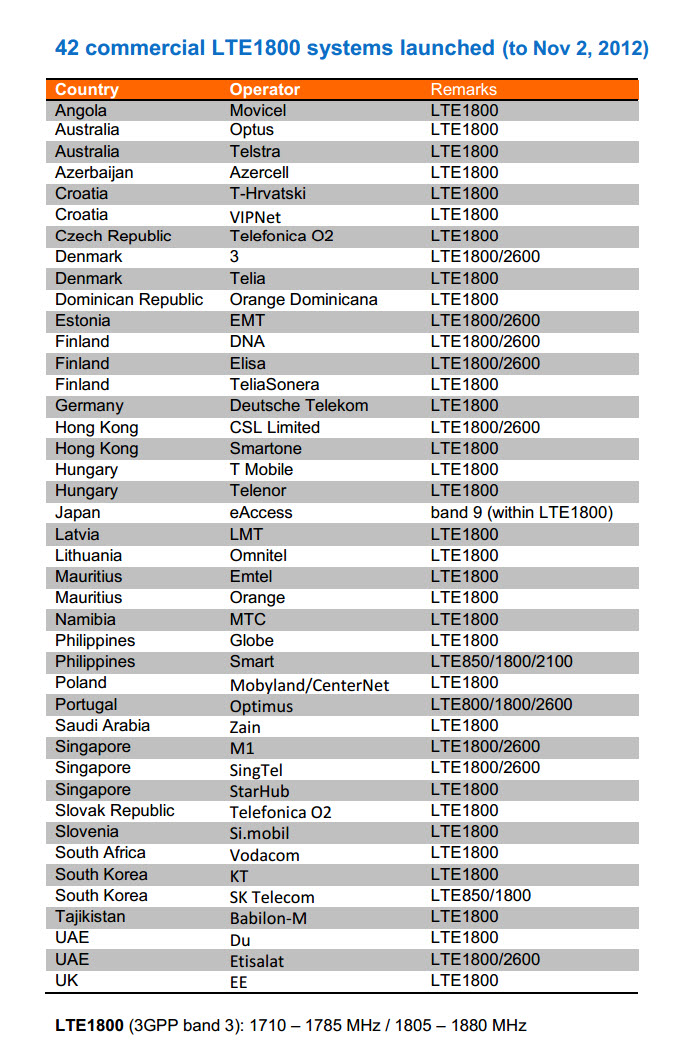
- First, confirm your local 4G LTE Frequency band, if you don’t know, please refer to below the two links:
A.) List_of_LTE_networks: http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/List_of_LTE_networks (check LTE Bands)
B.) 4G Map: http://ltemaps.org/home/ (check LTE network bands and status)
(Note: most of the information from the two links are right, but not all)
- After confirmation,you must make sure the local 4g LTE network is already launched to commerce. If not, there is no 4G network available there.
- Choose the right 4G USB modem which would work for this band. Here we have one option for you: 4G Mobile Broadband Shopping Mall (www.4gltemall.com )
To make it clear, here is another example to explain. Supposing you are living in Sweden, after check, we found the LTE frequency bands as below:
- Band 7 (2600 MHz) Deployed by Telenor/ Tele2 / Net4Mobility / TeliaSonera
- Band 20 (800 MHz) Deployed by TeliaSonera
- Band 8 (900 MHz) Deployed by Telenor/ Tele2 / Net4Mobility
So you can choose any 4G USB Modem that can work for LTE FDD 2600Mhz. And to use TeliaSonera, the modem must support 800Mhz if don’t support 2600Mhz. From this point, you can find that Samsung has two 4G LTE Surfstick named GT-B3730 and GT-B3740. GT-B3730 works on 4G FDD 2600Mhz and 3g 2100Mhz while GT-B3740 only works on 4G FDD 800Mhz, no 3G. So if you like Samsung, you may check whether the two 4G Modem works in your country.
You can check there are many models on 4G Mobile Broadband Shopping Mall that can work for this band, such as ZTE MF820, HUAWEI E392, E398, SIERRA Wireless 320U etc…

And please confirm the the band is LTE TDD or FDD, because there may be TDD 2600Mhz. It’s special band for TD-LTE network, FDD 2600Mhz modem can’t work on this.
It’s clear now. But if your 4G Network is WiMax, there is few options now. We suggest you follow your provider now, perhaps in near future, you can follow my method to choose what you like. Good luck.