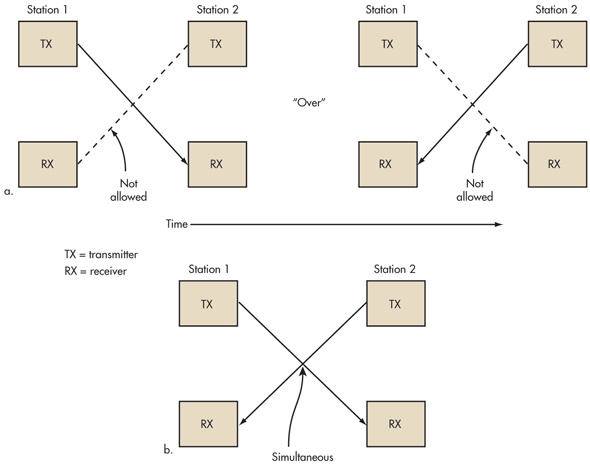
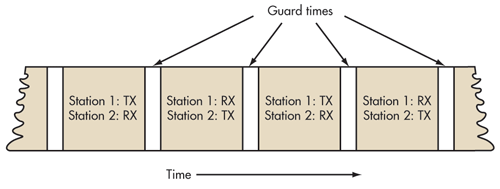
LTE is available in two technical variants: TDD and FDD. TDD stands for the English expression Time Division Duplex.FDD stands for the English word Frequency Division Duplex. It sounds complicated, but you can explain it simply: When FDD there are two channels, which is broadcast on: on one which you receive messages with their laptop or smartphone and on the other which you send the message. In TDD there is only one channel – it will be used alternately to send and receive. Transmit and receive mode switch it so fast that you do not notice. What are the advantages and disadvantages of both techniques?
The advantages and disadvantages of the techniques
FDD seems better at functions where many data are simultaneously transmitted and received – they both have their own supervised channel. One example would be telephone calls or video calls. Another benefit: When building the base stations need to take any further precautions – as transmit and receive channels are different, disrupt the channels of two base stations are not mutually exclusive. In TDD networks have to ensure that adjacent base stations do not interfere with each other.
Conversely, TDD uses the available space in the radio room much better. Often more data is received than sent, or more sent than received – for example, if I put a video on the Internet or send a friend a photo collection. In these cases – in technical terms, these are asymmetrical applications – TDD divides the space to send or receive on demand. Overall, the introduction of this TDD technology is cheaper, among other reasons, because the mobile operators do not have to hire as much radio room from the state as in FDD. The TDD needs only one channel and not two. For operators who previously used the wireless technology WiMAX, the transition to LTE TDD, with a lower price.
FDD and TDD: Worldwide both lay sometime par
Currently, the FDD technology is well forward, but with increasing global expansion of LTE networks, two techniques are commonly used equally well. The currently existing LTE networks in Germany, Austria, Scandinavia and the Baltic use FDD-LTE. Even Verizon Wireless in the U.S. uses this variant.
However, LTE is in TDD variant currently being tested by E-Plus in Germany. LTE TDD has also been tested in France, Ireland, Poland; the United States has the Wimax operator Clearwire tested. And WiMAX is interested in the technology in Japan, Saudi Arabia, Oman and Taiwan.
In South Korea, the Korean SK Telecom in early July has taken a LTE network on TDD base into operation in Malaysia still 2011; a TDD-LTE network will be built. Russia wants the operator Yota use a nationwide 180 cities comprehensive LTE network TDD. Experts believe that China has in each case; the TDD variant will be used for LTE, as well as in India.