5G Devices
What is 5G?
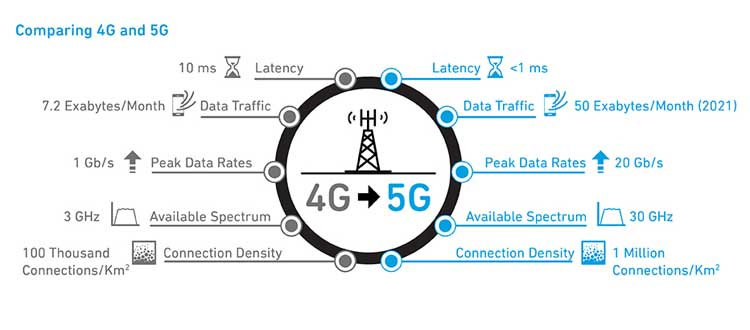
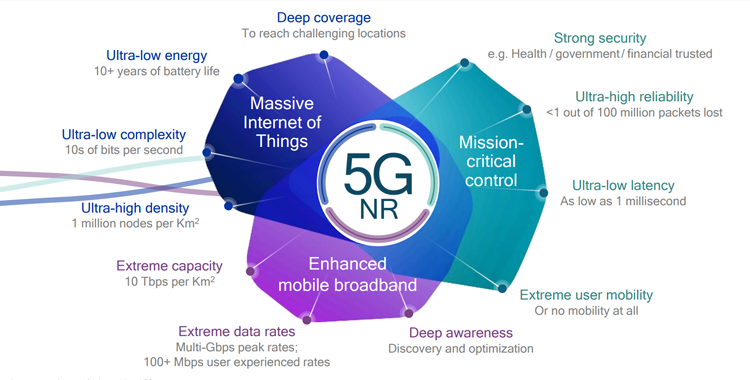
5G (fifth-generation wireless) is the latest iteration of cellular technology, and the upcoming evolution of wireless 4G LTE, which is mostly used today for wireless mobile networks. 5G is engineered to greatly increase the speed and responsiveness of wireless networks. It offers incredibly fast wireless communication that can be used to transmit all sorts of data at rates as high as 20 Gbps by some estimates -- exceeding wireline network speeds -- as well as offer latency of 1 ms or lower for uses that require real-time feedback. 5G networks offer more reliable connections on smartphones and other devices than ever before. The networks will help power a huge rise in the Internet of Things technology, providing the infrastructure needed to carry huge amounts of data, allowing for a smarter and more connected world.

Apart from fast mobile networks, 5G will also be used to deliver internet to your home. Its speed is also suited for upcoming technologies, such as providing a continuous stream of data required for many self-driving-car systems. With development well underway, 5G networks are expected to launch across the world by 2020, working alongside existing 3G and 4G technology to provide speedier connections that stay online no matter where you are.
What will we benefit from 5G?
- > Faster download and upload speeds
- > Smoother streaming of online content
- > Higher-quality voice and video calls
- > More reliable mobile connections
- > Greater number of connected IoT devices
- > An expansion of advanced technologies - including self-driving cars and smart cities
How fast could the 5G reach?
It’s still not exactly known how much faster 5G will be than 4G, as much of the technology is still under development. Most estimates expect the average speed of 5G networks to reach 10Gb/s, and some even think transfer rates could reach a whopping 800Gb/s. This would mean that users could download a full-length HD quality film in a matter of seconds and that downloading and installing software upgrades would be completed much faster than today.
How does 5G Work?
Wireless networks are composed of cell sites divided into sectors that send data through radio waves. Fourth-generation (4G) Long-Term Evolution (LTE) wireless technology provides the foundation for 5G. Unlike 4G, which requires large, high-power cell towers to radiate signals over longer distances, 5G wireless signals will be transmitted via large numbers of small cell stations located in places like light poles or building roofs. The use of multiple small cells is necessary because the millimeter wave spectrum -- the band of spectrum between 30 GHz and 300 GHz that 5G relies on to generate high speeds -- can only travel over short distances and is subject to interference from weather and physical obstacles, like buildings.
Previous generations of wireless technology have used lower-frequency bands of spectrum. To offset millimeter wave challenges relating to distance and interference, the wireless industry is also considering the use of lower-frequency spectrum for 5G networks so network operators could use the spectrum they already own to build out their new networks. Lower-frequency spectrum reaches greater distances but has lower speed and capacity than millimeter wave, however.
5G Frequency Bands
On 21st December 2017, in Lisbon, the 3GPP TSG RAN Plenary Meeting successfully approved first implementable 5G NR specification. The completion of the first 5G NR standard enables the full-scale development of 5G NR for large-scale trials and commercial deployments as early as in 2019. This first specification was completed as part of 3GPP Release 15.
As per 3GPP release 15, the frequency bands for 5G NR have been designated and TS 38.104 section 5.2 provides the list of bands in which 5G NR can operate. The specification defines the frequency bands as FR1 and FR2.
|
Band |
Frequency |
Type |
|
FR1 |
450 to 6000 MHz |
Sub-6 GHz |
|
FR2 |
24250 to 52600 MHz |
mm-Wave |
FR1 and FR2 are the basic frequency band classifications for 5G-NR. These can be further classified into three bands:
- Frequency Division Duplex Bands (FDD)
- Time Division Duplex Bands (TDD)
- Supplementary Bands: Supplementary Downlink Bands (SDL) & Supplementary Uplink Bands (SUL)
FR1 FDD (Frequency Division Duplex) Frequency Bands for 5G-New Radio
|
5G NR Band |
Uplink Frequency |
Downlink Frequency |
Bandwidth |
|
n1 |
1920 -1989 MHz |
2110 - 2170 MHz |
60 MHz |
|
n2 |
1850 - 1910 MHz |
1930 - 1990 MHz |
60 MHz |
|
n3 |
1710 - 1785 MHz |
1805 - 1880 MHz |
75 MHz |
|
n5 |
824 - 849 MHz |
869 - 894 MHz |
25 MHz |
|
n7 |
2500 - 2670 MHz |
2620 - 2690 MHz |
70 MHz |
|
n8 |
880 - 915 MHz |
925 - 960 MHz |
35 MHz |
|
n20 |
832 - 862 MHz |
791 - 821 MHz |
30 MHz |
|
n28 |
703 - 748 MHz |
758 - 803 MHz |
45 MHz |
|
n66 |
1710 - 1780 MHz |
2110 - 2200 MHz |
90 MHz |
|
n70 |
1695 - 1710 MHz |
1995 - 2020 MHz |
15/25 MHz |
|
n71 |
663 - 698 MHz |
617 - 652 MHz |
35 MHz |
|
n74 |
1427 - 1470 MHz |
1475 - 1518 MHz |
43 MHz |
FR1 TDD (Time Division Duplex) Frequency Bands for 5G-New Radio
|
5G NR Band |
Uplink Frequency |
Downlink Frequency |
Bandwidth |
|
n38 |
2570 - 2620 MHz |
2570 - 2620 MHz |
50 MHz |
|
n41 |
2469 - 2690 MHz |
2496 - 2690 MHz |
194 MHz |
|
n50 |
1431 - 1517 MHz |
1432 - 1517 MHz |
85 MHz |
|
n51 |
1427 - 1432 MHz |
1427 - 1432 MHz |
5 MHz |
|
n77 |
3300 - 4200 MHz |
3300 - 4200 MHz |
900 MHz |
|
n78 |
3300 - 3800 MHz |
3300 - 3800 MHz |
500 MHz |
|
n79 |
4400 - 5000 MHz |
4400 - 5000 MHz |
600 MHz |
FR1 Supplementary Downlink Bands (SDL) & Supplementary Uplink Bands (SUL) for 5G-New Radio
|
5G NR Band |
Uplink Frequency |
Downlink Frequency |
Bandwidth |
Type |
|
n75 |
- |
1432 - 1517 MHz |
85 MHz |
SDL |
|
n76 |
- |
1427 - 1432 MHz |
5 MHz |
SDL |
|
n80 |
1710 - 1785 MHz |
- |
75 MHz |
SUL |
|
n81 |
880 - 915 MHz |
- |
35 MHz |
SUL |
|
n82 |
832 - 862 MHz |
- |
30 MHz |
SUL |
|
n83 |
703 - 748 MHz |
- |
45 MHz |
SUL |
|
n84 |
1920 - 1980 MHz |
- |
60 MHz |
SUL |
5G NR Frequency Bands in FR2
|
5G NR Band |
Band Alias |
Uplink Band |
Downlink Band |
Bandwidth |
Type |
|
n257 |
28 GHz |
26.5 - 29.5 GHz |
26.5 - 29.5 GHz |
3 GHz |
TDD |
|
n258 |
26 GHz |
24.250 - 27.5 GHz |
24.250 - 27.5 GHz |
3.250 GHz |
TDD |
|
n260 |
39 GHz |
37 - 40 GHz |
37 - 40 GHz |
3 GHz |
TDD |
5G Applications
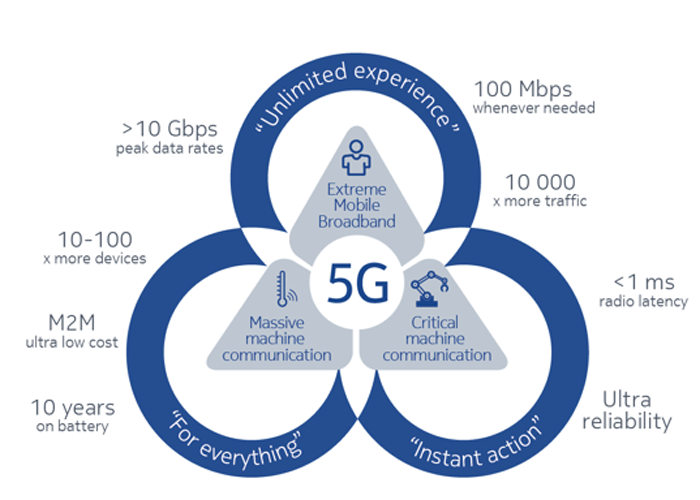
5G’s speed and reduced latency have the potential to transform entire industries.

Cars
Connected cars are a key growth driver. Futurists predict that the self-driving vehicles of the future will exchange cloud management info, sensor data, and multimedia content with one another over low-latency networks. According to ABI Research, 67 million automotive 5G vehicle subscriptions will be active, three million of which will be low latency connections mainly deployed in autonomous cars.
IoT
According to Asha Keddy, general manager of mobile standards for advance tech at Intel, 5G will be the first network designed with the Internet of Things (IoT) in mind. “These next-generation networks and standards will need to solve a more complex challenge of combining communications and computing together,” Keddy told Quartz in an interview ahead of the 2017 Mobile World Congress. “With 5G, we’ll see computing capabilities getting fused with communications everywhere, so trillions of things like wearable devices don’t have to worry about computing power because the network can do any processing needed.” Eventually, everything from wearables to internet-connected things such as washing machines, smart meters, traffic cameras, and even trees with tiny sensors could be connected.
Virtual reality and augmented reality
5G could bring about advances in virtual reality and streaming video. Sprint recently demonstrated streaming wireless VR at the Copa America soccer tournament, and Huawei showed a demo of 360-degree video streamed live from a 5G network.
Cloud-powered apps
Remote storage and web apps stand to benefit from 5G. “The cloud becomes an infinite extension of your phone’s storage,” El-Kadi said. “You never have to worry about running out of photo space.”
In addition to additional phone storage, you may see a significant difference in mobile hardware design overall. With 5G many of the computing tasks completed on your device can be moved to the network. Since the devices will not require the same computing capabilities, we may see so-called “dummy phones” with minimal hardware using the network to complete tasks. The transfer of power from the device to the network also means that your cell phone may have greater longevity as it will not necessarily require incremental hardware improvements to keep pace.
-
Fibocom SC161 5G Smart Module
* Fibocom 5G Smart Module
* Operating System:Android R
* Package: 433 LGA pin
* Support 5G Sub-6/4G LTE/WCDMA networks
* DL 1.9Gbps, UL 750Mbps
* Wi-Fi: 802.11 a/b/g/n/ac, 2.4G/5G,11 ax ready, 2X2 MIMO
* Target market: China
Learn More -
Fibocom FG360-NA 5G Module
* Platform: MT T750
* Support 5G SA/NSA dula-mode and NR CA
* Form Factor: LGA
* GNSS: GPS/GLONASS/Beidou/Galileo/QZSS
* DL: 4.13Gbps, UL 1.6Gbps
Learn More -
Fibocom FG360-EAU 5G Module
* Tarket market: Asia, Europe, Australia
* Support 5G SA/NSA dula-mode and NR CA
* Form Factor: LGA
* GNSS: GPS/GLONASS/Beidou/Galileo/QZSS
* DL: 4.13Gbps, UL 1.6Gbps
Learn More -
Fibocom FM150-AE 5G Module
* Chipset: Qualcomm SDX55
* Form Factor: M.2
* GNSS: GPS/GLONASS/Beidou/Galileo
* Support 5G SA/NSA networks
* 5G DL 2.1Gbps, UL 900Mbps
Learn MoreRegular Price: $799.00
Special Price $599.00
-
Fibocom AN958-EAU 5G C-V2X Module
* Chipest: Qualcomm SA515M
* Form Factor: LGA
* Support 5G Sub-6/4G LTE/WCDMA/GSM networks
* Antenna: 6 Antennas + 1GPS
* GNSS: GPS/GLONASS/GALILEO/BEIDOU
* 5G: Max 2.12Gbps(DL)/900Mbps & 450Mbps (UL)
Learn More -
Fibocom AN958-AE 5G C-V2X Module
* Chipset: Qualcomm SA515M
* Form Factor: LGA
* Support 5G Sub-6/4G LTE/WCDMA/TD-SCDMA/GSM networks
* Antenna: 6 Antennas + 1GPS
* GNSS: GPS/GLONASS/GALILEO/BEIDOU
* 5G: Max 1.6Gbps(DL)/NSA 600Mbps & SA 450Mbps (UL)
* Target region: Asia, Australia
Learn More -
Quectel RM502Q-GL 5G sub-6GHz module
* Form factor: M.2
* Supports both NSA and SA modes
* USB 3.1 / PCIe 3.0 high speed interface
* Multi-constellation GNSS receiver available
* Speeds: DL 5Gbps, UL 650Mbps
Learn More -
Quectel RG502Q-EA 5G sub-6GHz module
* Form factor: LGA
* Supports both NSA and SA modes
* Supports Option 3x, 3a and Option 2 network architecture
* USB 3.1 / PCIe 3.0 high speed interface
* Multi-constellation GNSS receiver available
* Speeds: DL 5Gbps, UL 900Mbps
Learn More$699.00 -
Foxconn T99W175 Lenovo 5G WWAN Card
* Lenovo 5G WWAN card
* Chipset: Qualcomm Snapdragon X55
* Form factor: PCIe M.2
* GNSS: GPS/Glonass/Beidou/Galileo
Learn More$399.00 -
Telit FN982m 5G NR M.2 Module
* Chipset: Qualcomm/SDX55
* Form factor: M.2
* Interfaces:USB 3.1 Gen 2 / Serial
* 4G Cat 20 up to 7 CA
Learn More -
Telit Cinterion MV31-W 5G Module
* Global 5G coverage on one single SKU
* LTE Cat. 20 fallback
* LTE Advanced-Pro (3GPP Release 15)
* Dual SIM support with Dual Standby Single Active support
* GNSS: GPS, GLONASS, Galileo and Beidou
Learn More -
ZTE MU5001 MU5001U 5G Mobile WiFi6 Router
* Chipset: Qualcomm SDX55
* Support 5G Sub5 technology
* WiFi 6 AX1800, 802.11b/g/n/ac/ax, dual band 2.4GHz/5GHz
* WiFi support up to 32 users
* Interfaces: 1 x Gigabit Ethernet Port + 1 type-C 3.1 port
Learn More -
Samsung Galaxy F52 5G SM-E5260
* 6.6 inches, 1080 x 2408 pixels TFT touchscreen, 120Hz
* Android 11, One UI 3.1, Qualcomm SM7225 Snapdragon 750G 5G (8 nm) chipset
* Quad(64MP + 8MP + 2MP + 2MP)main camera and single 16MP front camera
* Wi-Fi 802.11 a/b/g/n/ac, dual-band, Wi-Fi Direct, hotspot
* Non-removable Li-Po 4500 mAh battery
Learn More -
OPPO Reno6 5G
* 6.43 inches, 1080 x 2400 pixels, Android 11/ColorOS 11.3
* Chipset: MediaTek MT6877 Dimensity 900 5G (6 nm)
* Dual SIM(Nano-sim), 128GB 8GB RAM, 256GB 12GB RAM
* Triple(64MP + 8MP + 2MP) main camera/Single(32MP) front camera
* Non-removable Li-Po 4300 mAh battery
Learn More -
OPPO Reno6 Pro 5G
* 6.55 inches, 1080 x 2400 pixels, Android 11/ColorOS 11.3
* Chipset: MediaTek MT6893 Dimensity 1200 5G (6 nm)
* Dual SIM(Nano-sim), 128GB 8GB RAM, 256GB 12GB RAM
* Quad(64MP + 8MP + 2MP + 2MP) main camera/Single(32MP) front camera
* Non-removable Li-Po 4500 mAh battery
Learn More -
OPPO Reno6 Pro+ 5G
* 6.55 inches, 1080 x 2400 pixels, Android 11/ColorOS 11.3
* Chipset: Qualcomm SM8250-AC Snapdragon 870 5G (7 nm)
* Dual SIM(Nano-sim), 128GB 8GB RAM, 256GB 12GB RAM
* Quad(50MP + 13MP + 16MP + 2MP) main camera/Single(32MP) front camera
* Non-removable Li-Po 4500 mAh battery
Learn More -
OPPO K9 5G
* 6.43 inches, 1080 x 2400 pixels, Android 11/ColorOS 11.1
* Chipset: Qualcomm SM7250-AC Snapdragon 768G 5G (7 nm)
* Dual SIM(Nano-sim), 128GB 8GB RAM, 256GB 8GB RAM
* Triple(64MP + 8MP + 2MP) main camera/Single(32MP) front camera
* Non-removable Li-Po 4300 mAh battery
Learn More -
OPPO A53 5G
* 6.52 inches, 720 x 1600 pixels, Android 11/ColorOS 11.1
* Chipset: MediaTek MT6833 Dimensity 700 5G (7 nm)
* Dual SIM(Nano-sim), 128GB 6GB RAM, 128GB 4GB RAM
* Triple(13MP + 2MP + 2MP) main camera/Single(8MP) front camera
* Non-removable Li-Po 5000 mAh battery
Learn More -
OPPO A95 5G
* 6.43 inches, 1080 x 2400 pixels, Android 11/ColorOS 11.1
* Chipset: MediaTek MT6853 Dimensity 800U 5G (7 nm)
* Dual SIM(Nano-sim), 128GB 8GB RAM, 256GB 8GB RAM
* Triple(48MP + 8MP + 2MP) main camera/Single(16MP) front camera
* Non-removable Li-Po 4310 mAh battery
Learn More -
Honor Play5 5G
* Honor 5G Cell Phone* 5G Dual-mode(SA/NSA)
* 6.53 inches, 1080 x 2400pixels, Android 10, Magic UI 4.0
* Chipset: MediaTek MT6853 Dimensity 800U 5G (7 nm)
* 128GB 8GB RAM, 256GB 8GB RAM, dual-sim(Nano-sim)
* Quad(64MP + 8MP + 2MP + 2MP) main camera/Single(16MP) front camera
* Non-removable Li-Po 3800 mAh battery
Learn More