| Operator | Duplexing | Spectrum |
| Omnitel (TeliaSonera) | FDD | 1800 MHz, 2600 MHz |
| Bite | 2600 MHz | |
| Tele2 | 2600 MHz |
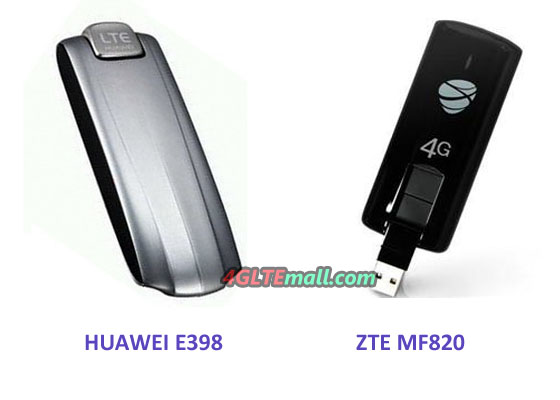
Will you buy HUAWEI E398u-11 or ZTE MF820 for your 4G LTE Modem?
As the top telecommunication equipment suppliers in China, ZTE and Huawei are always competing from 3G to 4G market. To share the global market, they may release similar telecom products for wireless network. Huawei E398u-11 4G LTE Surfstick and ZTE MF820 4G USB dongle are two similar modems that both works for 4G LTE FDD network band 1800/2100/2600MHz.
Then here comes the question: which one is better between Huawei E398u-11 and ZTE MF820 4G LTE USB Modem?
Appearance
From the appearance, they both in rotatable USB design and the modem body is somewhat bigger than common 3G USB dongles. Huawei E398u-11 seems cooler because the design is inspired by luxury car.
External Antenna Connector
There are two external antenna connectors in HUAWEI E398u-11 but there is no external antenna port in ZTE MF820. With 2 x 2 MIMO antenna, the speed would be double or may even triple faster.
Operation
If you want to plug 4G SIM card to the modem ZTE MF820, you need to open the whole back cover of MF820. And according the writer’s experience, the design is not user-friendly, because the first question is you don’t know where to open it, second, after you find the little cap to open, you may be unable to open it if you don’t too much effort. And you must two hands together to work. But if taking too much effort, you may worry to break the modem. You will never wish to break the modem before using it.
In this case, Huawei E398u-11 is easy to operate. There is only a short cap of a third of back cover. One hand can open it easily.
Mobile partner operation
Most of HUAWEI E398u-11 4G Modem is with mobile partner, like ZTE, it also has its own operation software. Both of them would take a little bit long time to install and get ready for connection. With large firmware, sometimes, they may let your PC run very slowly. But I personally like HUAWEI mobile partner more, because it seems HUAWEI Mobile partner is more simple and easier to setup than ZTE.
Connection speed
HUAWEI E398u-11 and ZTE MF820 could both connect in few seconds, actually, it may depends on the external network situation to determine which could connects faster. Under the same condition, HUAWEI E398u-11 may connect faster than ZTE MF820 for only 2-4 seconds, usually, we can’t notice that.
The above factors are important for a user to choose a 4G LTE USB modem, but it seems the two modems are equal to buy. HUAWEI E398u-11 is just better in appearance and antenna function, other factors are almost same, in this case, users can choose per their preference. If you like cool model and better signal and speed to surf, you should choose HUAWEI E398u-11, but if you want practical modem with better price, ZTE MF820 should be taken into your consideration.
If you want to have more options for 4G LTE USB dongles, please check http://www.4gltemall.com/4g-usb-modem.html .
4G LTE Spectrum in Latvija (Latvia)
| Operator | Duplexing |
Spectrum
|
| LMT – Latvijas Mobilais Telefons (TeliaSonera) | FDD | 1800MHz |
|
Bite
|
FDD | 2600MHz |
|
Tele2
|
FDD | 2600MHz |
| Triatel | 450 MHz, 800 MHz |
4G LTE Spectrum in Estonia (Eesti)
| Operator | Duplexing |
Spectrum
|
| Elisa | FDD | 1800 MHz, 2600 MHz |
| Tele2 | FDD | 2600 MHz |
| EMT(TeliaSonera) | TDD,FDD | 1800 MHz, 2600 MHz |
4G LTE Spectrum in Slovenia (Slovenija)
| Operator | Duplexing |
Spectrum
|
| Si.mobil | FDD | 1800MHz |
| T-2 | ||
| Mobitel | 800MHz,1800MHz,2600MHz |
4G LTE Spectrum in Croatia (Hrvatska)
| Operator | Duplexing | Spectrum |
| Hrvatski Telekom(T-Mobile) | FDD | 1800MHz |
| Tele2 Croatia | ||
| Vipnet(Telekom Austria) | FDD | 1800MHz |
4G LTE Spectrum in Hungary (Magyarorszag)
| Operator | Duplexing | Spectrum |
| T-Mobile Hungary | FDD | 1800MHz |
| Telenor Hungary | FDD | 1800MHz |
| Vodafone Hungary | TDD,FDD |
How to Configure HUAWEI E5151 Ethernet Mode Settings
Last time, we introduced how to set up the 3G connection for HUAWEI E5151 mobile WiFi, today, we will introduce how to Configure the Ethernet Settings for HUAWEI E5151:
To configure the Ethernet Settings, the first 6 steps are same as setting up 3G connection. But this time is not plug SIM card, you need to plug Ethernet cable this time.
1. Then after land to Quick setup page, click next and creat the Profile name.
2. Then click to next step to the Configure Ethernet Settings. Choose the connection toy you are using, the country, account name and password.
3. Click to next step, you come to the Page of setting SSID and encryption type and WiFi password.
4. After settings, click to next page to confirm and finish to connect.
In 3-5 seconds, you could find the WiFi signal coming from Huawei E5151.
This is the general and quick set up of Huawei E5151 for common users, if you want advanced functions from Huawei E5151, you need to configure in Advanced Settings. We will introduce later on www.4gltemall.com/blog/.
Huawei E5151 3G Configuration and Setup Steps
As a special member of Huawei E5 family, Huawei E5151 3G Mobile WLAN and Ethernet Router is more and more popular in businessmen and tourist. Some users may be in trouble of using it. And the main problem is that they don’t know how to set up Huawei E5151 and configure the connection. Today, we will have a general introduction of how to set up and configure this WLAN router E5151.
Set up 3G Wireless Connection
- Plug 3G SIM card to Huawei E5151
- Just one button to power on the E5151.
3. Connect the WiFi signal from E5151(the SSID is on the back cover )
4. Land the web management page, the address is 192.168.8.1 (the address is different from its predecessor Huawei E586 or Huawei E5331)
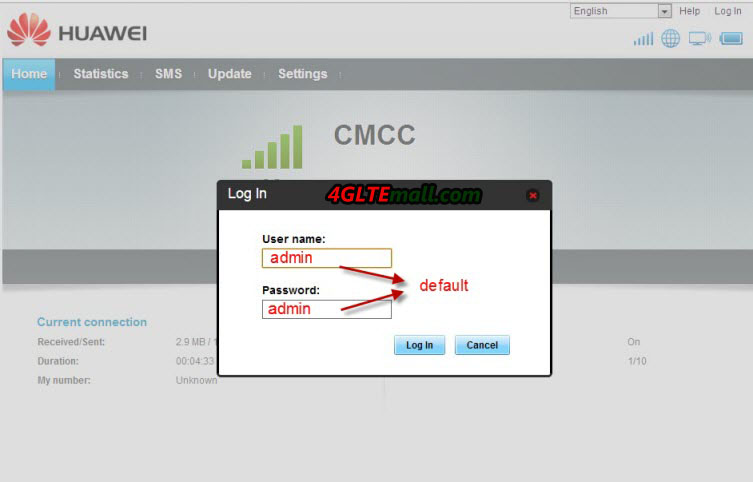
5. Log in to set up( Default log name and password are both “admin”
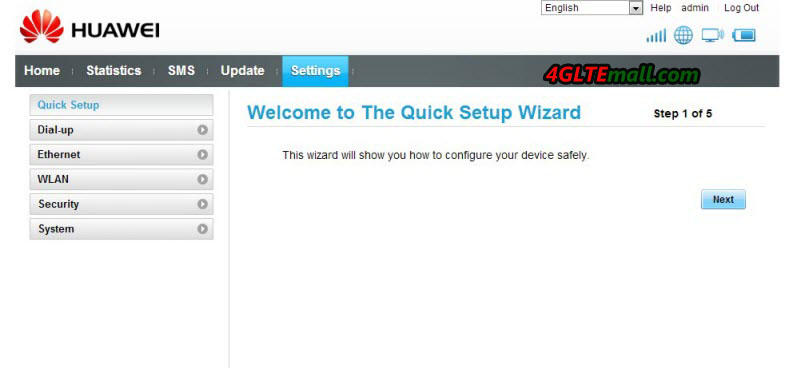
6. The page will guide you to the Settings. And you will find there is guide for Quick Setup
7. Click Next to next step. Usually, Huawei E5151 would auto identify you SIM card and operator, and automatically configure the corresponding data, you just need to click Next to next step.
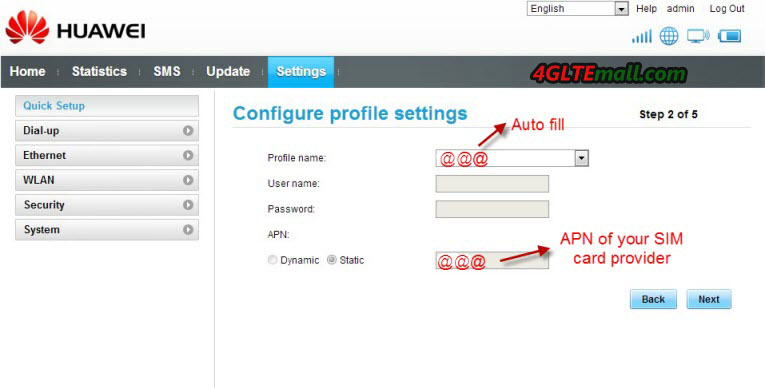
8. If not, you need to set up the Profile name, and APN of your provider. The profile can be any words, but APN must be right, it will determine whether you will get connected to network
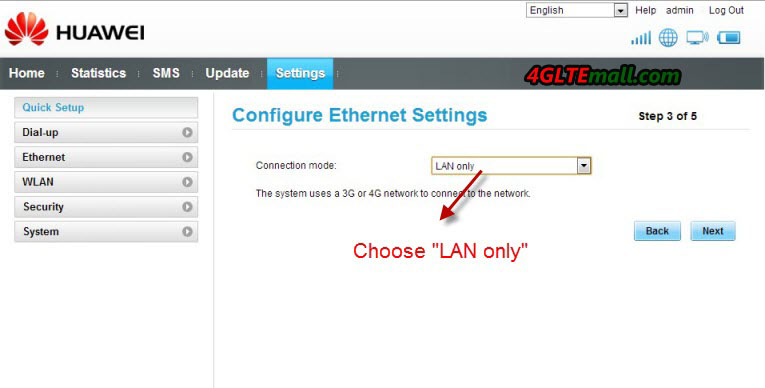
9. Then click Next to the page of Configure Ethernet Setting. Since we are set up 3G connection, in this step, you should choose “LAN only” in the connection type. Then to next page
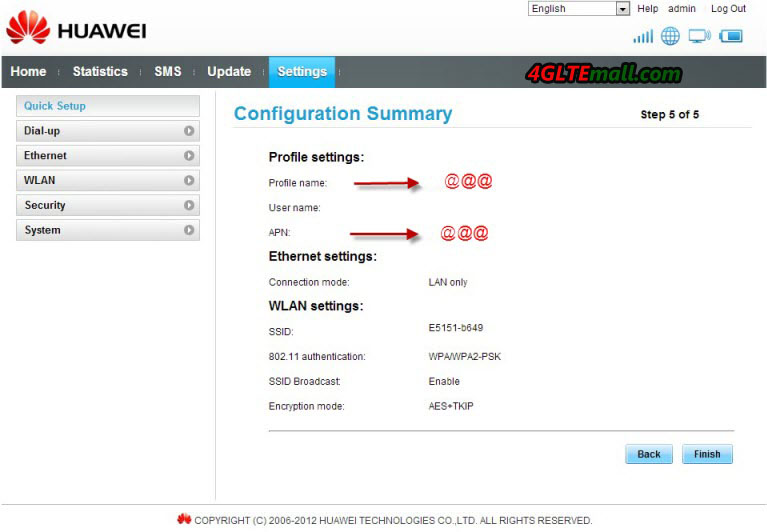
10. This step is to set up the SSID name and encryption password, you can set any name and password you like, but it would be better for you easily to remember them. Then click next to confirmation page. Click “Finish” and in 2 or 3 seconds, the E5151 could get connected with network and you can start surfing.
This is the general and quick set up of Huawei E5151 for common users, if you want advanced functions from Huawei E5151, you need to configure in Advanced Settings. We will introduce later on www.4gltemall.com/blog/.
To read more about:
How to configure HUAWEI E5151 Ethernet Mode Settings
EPC: A new core network for the new LTE radio technology
Many new transmission facilities to the cellular towers are visible part of the LTE structure.
The second, invisible to the public, is equally important part: The technology and infrastructure with which these new LTE transmission facilities are operated and controlled, the so-called core network, changes radically. This core network for LTE (Engineered packet-based core network) and Evolved Packet Core Evolved Packet or designated system. It basically works like the normal Internet, the technical term for this technology is an IP-based network or English an all-IP network. But what does that mean and how this network is different from a GSM network or a UMTS network, so what is the new in it?
GSM, UMTS and LTE networks: the differences
Put simply, the current mobile phone networks were completely fixed, or in large part on voice telephony. The GSM network, the second generation of mobile phone was originally designed as a pure network; other functions such as SMS and data transmission were then gradually it. The UMTS network calls and sending large amounts of data as equal functions together. The core network is divided into a part of UMTS, which provided fixed channels for the transmission of telephone calls (circuit switched) and one of the different data sets – like the Internet – transported.
The LTE network has – like the Internet – the absolute data priority. Telephoning is thus only one of many sub-functions of data transmission. A development is reconstructed, which is advanced in the fixed network have further calls is no longer handled through a separate channel, but runs as a Voice over IP over the Internet.
Which then affects the manner in which the LTE core network works: It is anything from one terminal to the other terminal to the Internet technology – are transmitted – the Internet Protocol, or IP. Technically speaking, it is an IP-based network or an all-IP network.
This fundamental change in the net makes the data transmission speed – both for downloading and sending, as well as in the reaction times. The Australian IT specialist Stuart Corner says: It is not primarily be the new LTE data radio technology, which allows high speed jumps, but most of all the new core network.
Signaling data: By registering for the bill
The new network is allocated differently: Over a part of running the so-called signaling data – for example, the registration of the participant in the network, its verification and identification, the location of their mobile device – the other part of the so-called user data – ie services that he accepts the scheme as phone or mobile Internet.
Among the parts that manage the signaling data and edit include Management Mobility Entity, short MME (Management of the mobile units), the Home Subscriber Server, short HSS (Subscriber Server) and the Policy and Charging Rules Function, briefly PCRF (fees office).
Logs in the MME to the mobile device, and then is forwarded to a location which the services – manages – ie the data transmissions. The MME also retrieves the information about the customer at HSS – because they are deposited there, in the GSM and UMTS networks had this customer database the name of Home Location Register (HLR). The PCRF can – depending on the rate – to specific data flows from that terminal or declines; it calculates how much the service costs at the rate reserved by the customer and shall issue an invoice.
User data: designing services funneled through the net
The services themselves are carried out in the so-called SAE gateway. The acronym stands for System Architecture Evolution Gateway – and said in German as the main interface for the network. This gateway consists of two areas: First, since the serving gateway is – short SGW in German about services portal. There the user’s terminal is managed by the application at the MME continues. It remains registered so when the user switches between two cell towers or when switching from LTE to a different wireless technology. It takes the data packets received by the user sends – for example by surfing – and forwards it to the exit.
The output is referred to as PDN Gateway, which is German for Public Data Network Gateway as portal to the public networks. And that is its function: Here the data to other networks – other mobile networks, Internet – forwarded and received the input data for the terminal of customers and forwarded.