According to the report from CNET, Ericsson announced yesterday that, as one part of the 5G wireless technology development plan, they get the peak transmission data rates to 5Gbps in a wireless test a couple of days ago.
This new is amazing if the wireless data rate reach to 5Gbps, which means the speed is 250 times faster than current LTE standard and it creates a new record for wireless link stream. Many corresponding terminals will benefit from this speed whatever smartphones, auto cars, medical and other equipments. Under the downstream of 5Gbps, it would take only 80 seconds to download a movie of 50GB, which is 5 times faster than the speed of 1Gbps from Google fiber.
However, it’s a pity that the 5Gbps link speed is only the speed under perfect laboratory environment and the real deployment of 5G network will start till 2020. Anyhow, this test speed provides theoretical support for future high wireless transmission.
Since the 5G test is under laboratory environment, there will be many works to do to universal this new network. Some professional people it’s too optimistic to deploy 5G network in 2020. But the sales management Johan Wibergh from Ericsson think it would be possible for users to access internet in this target speed, we must know it would bring a completely new network with high speed connection.
For Ericsson, it would be also important to get the test standard. In current wireless technology, Ericsson faces the great completion from Huawei, ZTE and other powerful vendors over the world. The latter already gain many market shares with aggressive price strategy. “This test proves, we will still be the leader from 4G network technology to 5G technology development, which is very important”, said Wibergh.
Ericsson had token the 5G network test with Japanese operator NTT Docomo, South Korea operator SK Telecom. And Ericsson indicates, the high penetration rate of LTE networks in North American market will introduces the 5G technology first. But no operator in North America has any word for 5G technology till now.
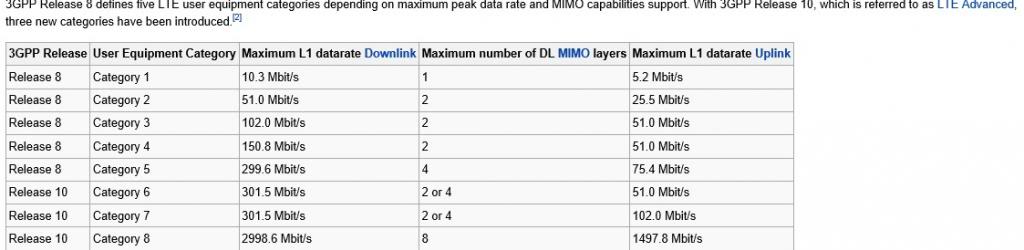
In Europe and Asia market, LTE is still the mainstream. Some ISPs are trying to test their LTE-Advanced network on LTE category 4 or better on LTE category 6, which support peak speed to 300Mbps. This speed is far less than 5G network speed, but with the development of network upgrade, we suppose 4G network will finally jumps to 5G and 5G will become the mainstream.