It would be lucky if you or your friend around have HUAWEI E5 Pocket WiFi Hotspot, you can easily share the wireless network via this device. As the world leading Pocket WiFi Hotspot, more and more people get to know the star from HUAWEI Portable 3G Router. When traveling, business trip, outdoor acctivities, you may feel enjoyable and convenient if you have a pocket WiFi HUAWEI E5.

So what is HUAWEI E5 Pocket WiFi? For Pocket WiFi, it’s easy to understand, but for HUAWEI E5, it could be a long but fantastic story.
HUAWEI E5, the original factory model should be E583X, was firstly released at at the Mobile World Congress in Barcelona in February 2009. Japan was the first country to introduce this mobile WiFi Hotspot(named HUAWEI E5830) to demestic and launched to commerce. As the developed market for electronics, Japanese like this portable 3G router very much, which made HUAWEI E5830 (The frist generation of HUAWEI E5 Pocket WiFi). Per the report from HUAWEI, the sales record of HUAWEI E5 pocket WiFi reached 300,000 units at the end of 2009. Now more than 40 networks operators are ordering HUAWEI E5 and introduce them to their domestic electronic users. Of course, they are not introducing the first generation of HUAWEI E5, HUAWEI have already launched 4th generation Pocket WiFi E5. Let us see what’s the stars of 4 generations.

First Generation– HUAWEI E583X(E5830, E5830S, E585, E583C, E560) 7.2Mbps Mobile WiFi Hotspot
As we introduced before, HUAWEI E583X opened the market for 3G Pocket WiFi based on its portability and easy use. The E5830s mobile Wi-Fi device connects to devices using its wireless interface, providing Internet access through any Wi-Fi device, mobile phone, game console, digital camera, notebook and PDA. Key features include: intelligent power control, temperature protection, web messages, web SD card information sharing, small screen page setting and screen display of statuses.
Huawei announced the launch of its next-generation mobile Wi-Fi device, the E583C in July 2010. Huawei developed the E585 based on feedback from consumers and UK wireless carrier Three, including a start-up button and OLED display detailing information such as signal strength, 3G or HSDPA connectivity, number of devices connected to the hub, battery level, and the network being used. This improvement makes HUAWEI E585 and E583C easier to operate and connection status more visible. They are equipped with a personal mobile WiFi hotspot to support maximum of 5 compatible devices. Sometimes, with USB cable, users can get one more device to access internet. These devices include notebooks, iPads, or handheld gaming consoles etc..

Huawei E583C Mobile 3G Router seems more popular because it adopts a new design with a 1-inch color OLED display that shows information such as network operator details, signal strength, Wi-Fi connection status, and battery level. And with the external antenna, users in rural area or low signal area could have external option to enhance their connection speed. The E583c converts 3.5G HSPA mobile signal into Wi-Fi coverage, automatically creating Internet access and individual Wi-Fi hotspots for up to five Wi-Fi-enabled digital devices. It can also provide simultaneous Internet access to a sixth device when it is connected to a laptop computer via a USB cable. HUAWEI E583c Pocket WiFi Router should be a revolution model fro HUAWEI because from this model, HUAWEI began to sell HUAWEI E5 with their own brand, but they maintain the channel with the operators. It’s a time of strategy change, HUAWEI want to build their own brand, not just the producer for operator carriers.

HUAWEI E560 Portable 3G Hotspot comes out recently, but seems it’s not a popular model because its price in high range and no more new style on this device, just copy the function of HUAWEI E585, and change appearance to HUAWEI E586, then E560 was born.
The key features of HUAWEI E5 first generation is that they support HSDPA 7.2Mbps and 5 WiFi enabled devices could share wireless network (one more via USB cable).
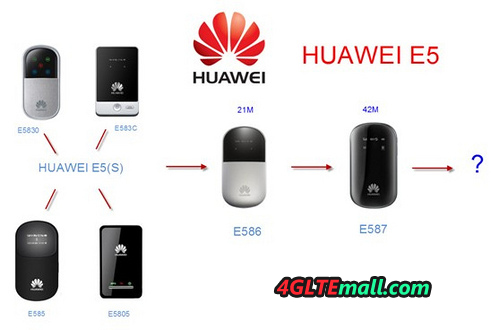
Second Generation– HUAWEI E586 E5331 E5332 E5151 3G HSPA+ 21Mbps Mobile WiFi Hotspot
With the network upgrade, there must be new devices to support the higher network. Then HUAWEI E5 second generation comes out. HUAWEI E586 Mobile WiFi Router was ther first model for 2nd generation. On 17 August 2011, UK Three announced its new high-speed mobile Wi-Fi device: the Huawei-built E586 MiFi, the first mobile Wi-Fi device in the UK to feature next generation HSPA+ mobile broadband technology.. But due to price, HUAWEI E586 3G WiFi Router seems not as popular as first generation models. If you use the device with contract, E586 is considerable. And there is branch model E586ES with external antenna ports.

New WiFi hotspots follow to meet customers’ preference. HUAWEI E5331 Mobile WiFi comes out with very good price and slim appearance, it soon become the best seller in Middle East and Europe. It supports HSPA+ data service up to 21.6Mbps and HSPA+ upload up to 5.76Mbps. With connection time in only 5 second, it becomes more attractive to the users who want easy setup and fast connection with high speed link. Few people know E5331 mobile HSPA+ router has a sister model HUAWEI E5332 with external antenna port. The main difference between them is the antenna. Other features are almost the same. Configured bands of E5331 and E5332 seem more appropriate for users in Europe and Africa.

There is one special E5 pocket WiFi HUAWEI E5151. HUAWEI E5151 pocket WiFi is different from other 2nd generation HUAWEI E5 models because besides the features of 3G UMTS bands and HSPA+ speed, E5151 has an Ethernet port to connect Ethernet cable, which can transfer the WLAN to WiFi signal. So to some extent, HUAWEI E5151 Pocket WiFi is a mobile WiFi and WLAN router.

In conclude, HUAWEI E5 2nd generation could support HSPA+ 21mbps and 5.76mbps, with support of 5 wifi users, with or without external antenna port.
Third Generation– HUAWEI E587 E5756 3G DC-HSPA+ Mobile WiFi Hotspot
Consumers always want the network moving faster, and the wireless terminals. And there HUAWEI E587 42Mbps Mobile WiFi comes into eyes. With external antenna port and larger battery capacity, HUAWEI E587 HSPA+ Pocket WiFi help the users who need high speed transmission or game player to experience much better. The workmanship of HUAWEI E587 Mobile WiFi is much more exquisite than previous model. Looking back to the old models, the path somewhat like iPhone, at the beginning, iPhone 1 or 2 are not that well know, from iPhone 3, it become hot among users. When iPhone 4 appears, it’s the hottest mobile phones in the markets. Comparing with iPhone 3, iPhone 4 has much better workmanship and many improvements in performance. HUAWEI E587 Mobile Router somewhat like iPhone 4. When you hand it, the feel is much different from normal pocket wifi.

Now, there is a new pocket WiFi Huawei E5756 42mbps WiFi hotspot available now. Due to lack of enough information, we can tell what the difference between HUAWEI E587 and E5756 is, but one point is clear that there must some improvements in E5756, we suppose it like HUAWEI E5331 with better internal design and better solution for users.

So the key features of the third generation of HUAWEI E5 family is download speed at HSPA+ 42Mbps and much better workmanship than predecessors.
Fourth Generation– HUAWEI E589 E5776 4G LTE Pocket WiFi Router
Since 4G LTE era comes, HUAWEI E5 Family develops new members to meet the requirements from networks and end users. HUAWEI E589 4G LTE Mobile Pocket WiFi comes to meet the demand and there is no doubt that HUAWEI E589 Portable 4G Router would attract many geeks or MiFi lovers’ eyes. HUAWEI E589 Support LTE download speed at 100Mbps, and support LTE FDD 900/1800/2100/2600Mhz, which almost covers all the 4G LTE networks all over the world. And in any countries deployed 4G LTE network, you can find available SIM card to use with HUAWEI E589 Pocket WiFi. That’s the most attractive core for HUAWEI E589. But it seems HUAWEI E589 4G LTE Router let consumers wait too long time. It’s expected to be available next month. Who knows…

HUAWEI E589 4G Router is not the end of HUAWEI E5, actually, HUAWEI released another HUAWEI E5 4G Pocket WiFi Hotspot with HUAWEI E589. The model number is HUAWEI E5776 4G Mobile WiFi Router, which support LTE donwload up to 150Mbps. What a amazing! The same features of HUAWEI E589 and E5776 is that they could both support up to 10 WiFi enabled devices, which is almost the double of the first generation of HUAWEI E5 Models.

So the fourth generation of HUAWEI E5 family is that they support 4G LTE network and upgrade of donwload speed. More up to 10 users could share the WiFi network.
We believe more and more HUAWEI E5 mobile devices would be available in near future. And more and more consumers will enjoy the wireless world brought from HUAWEI E5 Family.