You may know Huawei 4G smartphones from China, but do you know another Chinese manufacturer OnePlus? If you are looking for a smartphone with the best performance on LTE network, you should not miss a smartphone with Qualcomm Snapdragon 845 chipset and Snapdragon X20 modem. Although HiSilicon (Huawei) and Intel (eg Apple) offer very good modems, but the Qualcomm chipset is the most widespread in any case. The OnePlus 6 is currently one of the cheapest smartphones with Snapdragon 845 and still offers excellent features, so we will take a test in the LTE network.
OnePlus 6 Features
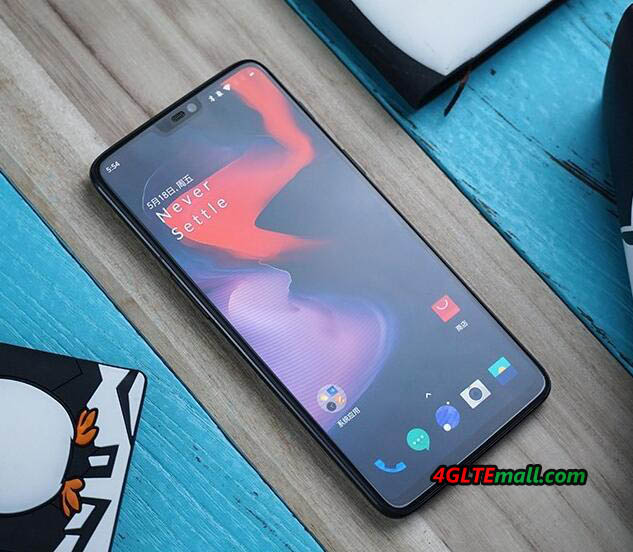
The OnePlus 6 comes with a 6.28 inch AMOLED screen, up to 8GB of RAM and up to 256GB of internal memory. It is dual-SIM capable and has a 3,300mAh battery – a quick-charger power adapter is included. On the back, you will find a dual camera with 16 or 20 megapixels, which shoots quite good pictures. It offers two unlock options: fingerprints unlock or face unlock.
OnePlus 6 Specifications
The OnePlus 6 is also offered in the online trade by Asian dealers in a version with the model number A6000 – this supports many, but not all major LTE frequency bands. The European or North American version has the model number A6003 and supports FDD LTE on frequency band 1/2/3/4/5/7/8/12/17/18/19/20/25/26/28/29/30/32/66/71 and TDD LTE on frequency band 34/38/39/40/41. Up to 1 GBit/s are possible in the downlink with quadruple-channel bundling (4CA), up to 150 MBit/s in the uplink via 2CA. 256QAM in the downlink, 64QAM in the uplink and 4 × 4 MIMO antenna technology are also supported. This makes the OnePlus 6 well equipped for use in LTE networks worldwide.
Admittedly, the OnePlus 6 is currently still the latest OnePlus smartphone, but the successor OnePlus 6T is now available on the market. The chipset and modem of OnePlus 6 should be identical to the successor 6T, but of course, there are some changes and improvement in the newer Oneplus 6T, which you should be curious.
Qualcomm Snapdragon 845 with X20 modem
The Qualcomm Snapdragon 845 is a system-on-a-chip (SoC), bringing together diverse chips such as processor and modem on a single chipset. The integrated Snapdragon X20 modem is especially relevant for this test. It is Qualcomm’s second-fastest commercially available LTE modem, only the X24 is even faster (currently not available in any SoC).
The X20 modem offers LTE Cat18 in the downlink and LTE Cat13 in the uplink and offers manufacturers the opportunity to theoretically bundle up to 5 frequency bands via carrier aggregation in the downlink. In the uplink, the modem is 2CA capable. The 4 × 4 MIMO antenna technology is possible on up to 3 carriers simultaneously. 256QAM modulation in the downlink and 64QAM modulation in the uplink are of course included.
In total, up to 1.2 Gbit/s in the downlink and up to 150 Mbit/s in the uplink can theoretically be achieved with a Snapdragon X20 modem. However, as described in the previous section, the OnePlus 6 is slightly slower because not all features of the X20 have been implemented, for example, OnePlus has eliminated 5CA and only uses 4CA.
OnePlus 6 Test in the LTE network
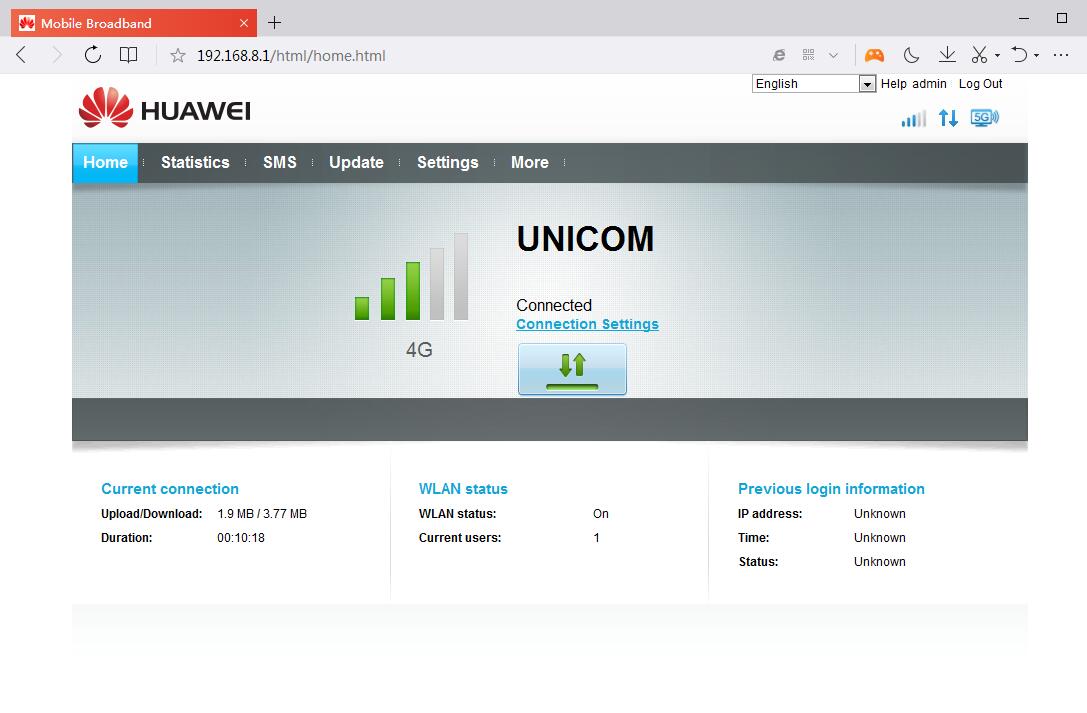
At the test site, LTE was available on Band 8 (900 MHz), Band 3 (1800 MHz) and Band 7 (2600 MHz) in the Vodafone network. On band 3, 4 × 4 MIMO antenna technology was used, and two carriers were used (10 MHz and 20 MHz). The modulation was at 256QAM in the downlink and 64QAM in the uplink. Band 8 was not usable for channel bundling, so Carrier Aggregation could only be used with B7 + B3 + B3. Theoretically, the combination of the individual technologies would have made it possible to achieve well over 300 MBit/s in the downlink – in practice, however, other simultaneous users in the cell will limit the speed in practice.
Just below 300 MBit/s in the downlink and about 60 MBit/s in the uplink could be achieved with the OnePlus 6 at different times and on different days. These are very good values, but a look in the Netmonitor revealed that the device had always bundled only two bands, ie B3 + B3 or B3 + B7. 3CA with B7 + B3 + B3 apparently cannot be used in the device with the LTE network. That’s a pity because it’s probably just a software configuration – the hardware should be fine.
Conclusion
The OnePlus 6 showed in the test a very good system performance and was able to score with a very good display and very good software. In many places, it became clear that the OnePlus product designers put a lot of emphasis on details, from the packaging to the stylish accessories to the sliding switch for the volume profile.
Unfortunately, the OnePlus 6 did not live up to expectations in tests in the LTE network, so the smartphone, unfortunately, did not support the CA combination B7 + B3 + B3 available at Vodafone, which is at slightly lower maximum speeds than, for example, the Apple iPhone Xs with Intel chipset resulted. The quality of reception was better than that of the iPhone and thanks to the 4 × 4 MIMO antenna technology; the OnePlus 6 is definitely well prepared for the future.