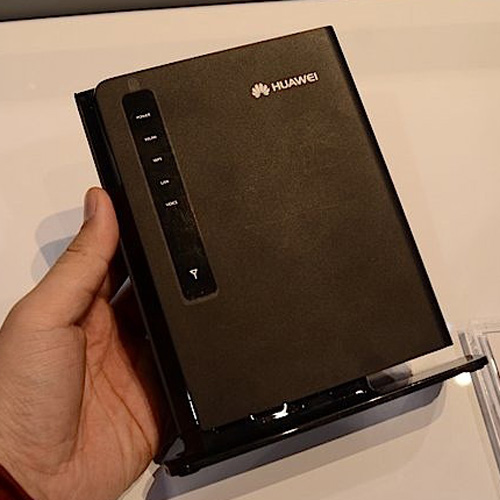
It has been a long time since Huawei E589 and Vodafone R210 available in the market. But there are still many users who haven’t gotten their 4G mobile WiFi.
Today, we will have a general review of the two similar 4G LTE mobile WiFi. Huawei released Huawei E589 at the beginning of 2012, then Vodafone customized this factory model per its preference, then Vodafone R210 was presented to public.
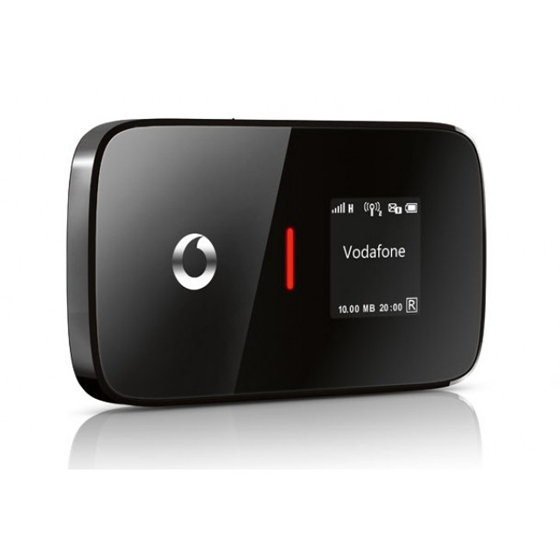
Vodafone R210 4G Pocket WiFi was first available in European areas for Vodafone 4G LTE network. With Vodafone logo below the screen, it looks cool. The classic combination of red and black color makes Vodafone R210 attractive. However, following the factory model of Huawei E589, Vodafone R210 has only one external antenna connector, which may not be a good solution for MIMO. The battery is inserted and cannot be detachable. But the battery is rechargeable with capacity of 3000mAh, which could support the R210 to work for 6 – 8 hours.
Here comes a question, what’s the key difference between Huawei E589 and Vodafone R210? Are they just different from the logo? It’s a good question.
Vodafone R210 is for the commercial 4G LTE network from Vodafone in Europe. So when Vodafone ordered R210, it set R210 to support its deployed 4G LTE frequency band 800/1800/2600MHz. However, Huawei E589 is the model in Huawei brand, so it’s not limited to any network, per the specification, we found it would work on 4G FDD 800/900/1800/2100/2600MHz, which covers almost 80% 4G FDD network available now. Based on good reputation in 3G mobile WiFi, Huawei E589 4G LTE pocket WiFi will lead the market demand.
So Huawei E589 would support more operators over the world, unlimited to Vodafone. Per current sales record, Huawei E589 is the most popular mobile WiFi for 4G LTE network, especially in Asia and Europe. The good news is that there are unlocked Vodafone R210 available in 4gltemall.com , it means Vodafone R210 could not only work with Vodafone 4G network, but also support the 4G FDD network operators in other countries or areas. And the price is better than Huawei E589, so if you like Vodafone R210, and don’t want contract, to buy an unlocked Vodafone R210 from 4gltemall.com is a good idea.